The Food, Mood & Poop Journal
(FMPJ)
A Comprehensive Tracking tool for Digestive Health
Introducing the Food, Mood, Poop Journal: A Comprehensive Tracking Tool for Digestive Health
When it comes to managing and improving digestive health, understanding the relationship between what we eat and how we feel is crucial. The Food, Mood, Poop Journal is an innovative tool designed to help individuals make these connections clearer. This journal allows us to track our daily dietary intake, mood variations, and bowel movements, providing invaluable insights into how different foods impact overall health and well-being.
Welcome to a transformative approach to understanding and improving your gut health—the Food, Mood, Poop Journal (FMPJ). This comprehensive tool is designed to help you discover the intricate connections between what you eat, how you feel, and the quality of your bowel movements. By tracking these critical elements, the FMPJ provides personalized insights that empower you to make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle, ultimately enhancing your overall well-being.
In functional wellness, we often emphasize the balance between various bodily systems. The FMPJ serves as a practical resource to help you apply this balance by observing and adjusting based on real-time feedback from your own body. Whether you're dealing with digestive discomfort, food sensitivities, or just aiming to optimize your health, this journal is your daily companion in the pursuit of a happier gut and a healthier life.
The FMPJ goes beyond traditional tracking by including essential components such as fat, fiber, protein, mood, bowel movements, and phytonutrients (eating the rainbow). Each of these elements plays a significant role in your digestive health and overall vitality:
1. Fat: Essential for energy, cell growth, and the absorption of vitamins. Monitoring fat intake helps balance healthy fats while limiting unhealthy ones.
2. Fiber: Crucial for regulating blood sugar levels, maintaining digestive health, and preventing diseases. Tracking fiber ensures adequate intake for optimal digestion.
3. Protein: The building blocks of the body, necessary for tissue repair, immune function, and overall cellular health. Monitoring protein intake supports muscle health and energy levels.
4. Mood: Recording mood variations helps identify patterns and triggers related to dietary intake, providing insights into emotional well-being.
5.Poop: Using the Bristol Stool Chart to track bowel movements helps monitor digestive health, highlighting potential issues and promoting timely interventions.
6. Phytonutrients (Eating the Rainbow): Ensuring a diverse intake of colorful fruits and vegetables provides a range of beneficial compounds that support overall health, from antioxidant properties to immune boosting effects.
By consistently monitoring these key aspects—fat, fiber, protein, mood, poop, and phytonutrients—you can gain valuable insights into how your diet and lifestyle choices impact your health, allowing you to make informed adjustments to improve your well-being.
Why Use the Food, Mood, Poop Journal?
The FMPJ is rooted in the understanding that our gut health is pivotal to our overall health. It acts as the control center for many bodily functions, influencing everything from our immune system to our mood and mental clarity. Here’s how the FMPJ helps you tap into your gut’s potential:
1. Track What You Eat: Documenting your daily food intake can shed light on how certain foods affect your digestive system and overall health. This record helps identify potential food intolerances or allergies that might be impacting your comfort and health.
2. Monitor Your Mood: The gut is often called the "second brain" because of its significant impact on our mood and emotional health through the gut-brain axis. By recording your mood, you can start to see patterns that link your dietary habits with emotional fluctuations.
3. Observe Your Poop: Your stool is a direct indicator of gut health. Regularly noting details about your bowel movements can help you quickly identify when things aren't as they should be, allowing for timely dietary adjustments.
4. Track Fat, Fiber, and Protein Intake Ensuring a balanced intake of these macronutrients is essential for optimal digestive health and overall well-being. Monitoring fat, fiber, and protein helps you maintain a diet that supports your body's needs, from energy levels to muscle health and digestive regularity.
5. Eat the Rainbow (Phytonutrients): Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your diet ensures you receive a broad spectrum of phytonutrients. These natural compounds have numerous health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune-boosting properties. Tracking your phytonutrient intake helps you ensure you're getting the full range of benefits from your diet.
6. Develop Personal Insights: Over time, the FMPJ will help you correlate specific foods with changes in mood and bowel health, enabling you to customize your diet for optimal health. By understanding these connections, you can make informed dietary and lifestyle adjustments to enhance your overall well-being.
By consistently using the Food, Mood, Poop Journal, you can gain valuable insights into your digestive health, make more informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle, and ultimately achieve better health and well-being.
Getting the Most Out of Your Journal
To effectively use the Food, Mood, Poop Journal, commit to making regular entries and be as detailed as possible. Consistency is key to uncovering patterns and making the necessary adjustments to improve your health. Each week, take time to review your entries, note any trends, and consider how you might adapt your diet and lifestyle to foster better gut health.
This journal not only serves as a daily log but also as a guide to educate you on the importance of each tracked aspect and how they interrelate.
The Food, Mood, Poop Journal is an invaluable resource for anyone looking to enhance their digestive health, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. By integrating this tool into your daily routine, you embark on a path of greater self-awareness and proactive health management, leading to a healthier, more balanced you.
Tips for Effective Use:
1. Be Consistent: Make entries at the same time each day, preferably after meals and at the end of the day, to ensure you capture accurate and relevant information.
2. Be Detailed: Include specifics about the foods you eat (types, quantities, preparation methods), your mood fluctuations (time of day, intensity), and bowel movements (frequency, consistency, color).
3. Review Weekly: Set aside time each week to review your journal entries. Look for patterns and correlations between your diet, mood, and bowel movements. This reflection can provide insights into what adjustments might be necessary.
4. Adjust Accordingly: Use the insights gained from your journal to make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle. Small changes can lead to significant improvements in your overall health.
5. Seek Professional Guidance: If you're unsure about your observations or need personalized advice, consider consulting a healthcare professional or a nutritionist who can help interpret your journal entries and provide tailored recommendations.
6. Stay Educated: Use the journal as a learning tool. Educate yourself on the importance of fat, fiber, protein, mood, and phytonutrients, and how they contribute to your digestive health and overall well-being.
By following these tips, you can maximize the benefits of the Food, Mood, Poop Journal and take proactive steps toward improving your gut health and overall quality of life.
Food Tracking
Dietary Awareness
Food tracking is a methodical approach to monitoring what you eat in order to understand and improve your health. It involves recording every item you consume, including meals, snacks, and beverages. This practice can help identify dietary patterns, recognize food intolerances or sensitivities, and ensure a balanced intake of nutrients. Here’s a detailed exploration of food tracking, its benefits, and how to effectively implement it.
Mood
The Missing Factors
The connection between the gut and the brain, often referred to as the gut-brain axis, underscores the profound impact our digestive health has on our mental state, and vice versa. By tracking our mood alongside our diet and bowel habits, we can uncover patterns and triggers that affect our emotional and physical health.


Poop
With good bacteria
Tracking what we consume gives us valuable insights into our dietary habits and their direct effects on our health. But to gain a complete picture, we must also observe what leaves our body. The old adage "crap in, crap out" reminds us of the importance of quality inputs for quality outputs, which is just as relevant to our digestive health as it is to data analysis. This week, by adding poop tracking to our regimen, we aim to close the loop on our body’s digestive narrative.
This page contains affiliate links. This means I may earn a commission should you choose to sign up for a program or make a purchase using my link.
Food Tracking
Enhancing Health through Dietary Awareness
Food tracking is a methodical approach to monitoring what you eat in order to understand and improve your health. It involves recording every item you consume, including meals, snacks, and beverages. This practice can help identify dietary patterns, recognize food intolerances or sensitivities, and ensure a balanced intake of nutrients. Here’s a detailed exploration of food tracking, its benefits, and how to effectively implement it.

Purpose of Food Tracking
The primary goal of food tracking is to gain a detailed understanding of your diet and its effects on your health. This information can be used to:
1. Identify Nutritional Gaps: Track your intake of various nutrients to ensure you're meeting your dietary needs. This can help you identify if you're lacking essential vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients and make necessary adjustments to your diet.
2. Manage Health Conditions: Understand how different foods impact medical conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or digestive issues. Food tracking can help you manage symptoms and make dietary choices that support your health.
3. Weight Management: Monitor calorie intake for weight loss, gain, or maintenance. By keeping a record of what you eat, you can ensure you're consuming the right amount of calories to meet your weight goals.
4. Discover Food Sensitivities: Notice patterns related to food sensitivities or allergies by correlating what you eat with how you feel physically and mentally. This can help you identify trigger foods and avoid them to improve your overall well-being.
5. Improve Eating Habits: Become more mindful of your eating habits, portion sizes, and meal timing. Food tracking encourages you to be conscious of what you eat, helping you develop healthier eating patterns and make better dietary choices.
By diligently tracking your food intake, you can gain valuable insights into your dietary habits and make informed decisions that enhance your overall health and well-being.
Benefits of Food Tracking
1. Increased Awareness: Keeping a food diary makes you more conscious of what you're eating. This heightened awareness can lead to healthier choices and better portion control, ultimately supporting your nutritional goals.
2. Data-Driven Insights: Over time, tracking provides valuable data that can highlight the impact of dietary changes and help tailor individualized nutrition plans. This information can guide you in making more effective adjustments to your diet.
3. Behavioral Change: Regular tracking can reinforce good eating habits and deter overeating or poor food choices. By consistently monitoring your intake, you are more likely to stay accountable and motivated to maintain a healthy diet.
4. Empowerment and Control: Understanding the relationship between food and health empowers individuals to make informed decisions that can control and improve their health outcomes. This sense of empowerment can lead to a more proactive approach to managing your diet and overall well-being.
By incorporating food tracking into your routine, you can experience these benefits and take a significant step toward improving your health and achieving your nutritional goals.
What to Track
Fat
Role in the Body:
Fats are essential macronutrients that provide energy, support cell growth, protect organs, and aid in the absorption of vital nutrients. They play a crucial role in hormone production and maintaining overall health.
Types of Fat:
- Unsaturated Fats: Found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil, these fats are beneficial for heart health and can help reduce inflammation
- Saturated Fats: Found in animal products like meat and dairy, these fats should be consumed in moderation as they can raise cholesterol levels.
- Trans Fats: Often found in processed foods, these should be avoided as they increase the risk of heart disease.
Why Track Fat?
Monitoring fat intake helps ensure you are consuming the right types and amounts of fat, balancing healthy fats while limiting unhealthy ones to support cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Fiber
Role in the Body:
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. It is crucial for maintaining digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and supporting heart health. Fiber also aids in satiety, helping to manage weight.
Types of Fiber:
- Soluble Fiber: Found in oats, apples, and beans, this type of fiber dissolves in water and can help lower glucose levels and blood cholesterol.
- Insoluble Fiber: Found in whole grains, nuts, and vegetables, this type of fiber helps food move through the digestive system and prevents constipation.
Why Track Fiber?:
Tracking fiber intake ensures you are getting enough to support healthy digestion, prevent chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease, and maintain overall digestive regularity.
Protein
Role in the Body:
Proteins are the building blocks of the body, essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. They play a role in the production of enzymes, hormones, and other body chemicals, and are necessary for immune function and muscle health.
Sources of Protein:
- Animal Sources: Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
- Plant Sources: Beans, lentils, tofu, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Why Track Protein?:
Monitoring protein intake helps ensure you are consuming adequate amounts to meet your body’s needs, especially for muscle repair and growth, immune support, and overall cellular health.
Phytonutrients (Eating the Rainbow)
Role in the Body:
Phytonutrients are natural compounds found in plant foods that provide a range of health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune-boosting properties. These compounds support overall health and can help protect against chronic diseases.
Color Categories and Benefits:
- Red: Lycopene (tomatoes, red peppers) – supports heart health.
- Orange: Beta-carotene (carrots, sweet potatoes) – supports vision and immune function.
- Yellow: Lutein and zeaxanthin (yellow peppers, corn) – supports eye health.
- Green: Chlorophyll, folate (spinach, kale) – supports detoxification and cellular health.
- Blue/Purple: Anthocyanins (blueberries, eggplant) – support brain health and reduce inflammation.
- White: Allicin (garlic, onions) – supports immune function and cardiovascular health.
Why Track Phytonutrients?:
Ensuring a diverse intake of colorful fruits and vegetables provides a wide spectrum of these beneficial compounds. Tracking phytonutrient intake helps you maximize the health benefits of a varied, plant-rich diet, supporting overall vitality and disease prevention.
By understanding the roles and benefits of fat, fiber, protein, and phytonutrients, you can make more informed dietary choices that support your digestive health and overall well-being.
Getting the Most Out of Your Journal
To effectively use the Food, Mood, Poop Journal, commit to making regular entries and be as detailed as possible. Consistency is key to uncovering patterns and making the necessary adjustments to improve your health. Each week, take time to review your entries, note any trends, and consider how you might adapt your diet and lifestyle to foster better gut health.
This journal not only serves as a daily log but also as a guide to educate you on the importance of each tracked aspect and how they interrelate.
The Food, Mood, Poop Journal is an invaluable resource for anyone looking to enhance their digestive health, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. By integrating this tool into your daily routine, you embark on a path of greater self-awareness and proactive health management, leading to a healthier, more balanced you
HOW TO TRACK FOOD EFFECTIVELY
Be Consistent: The key to successful food tracking is consistency. Aim to record your food intake every day to get a comprehensive view of your dietary habits.
Detail is Key: Include specifics such as the type of food, amount, preparation method, and timing of meals. The more detailed your entries, the more useful the data will be.
Use Tools and Apps: Many apps and tools are available to simplify food tracking. These can automatically calculate calorie intake, nutritional content, and offer insights based on your entries.
Review Regularly: Set a regular schedule to review your food diary. Look for patterns or trends that could be impacting your health, and adjust your diet accordingly.
Combine with Other Health Data: To enhance the benefits of food tracking, combine it with tracking other health metrics such as weight, mood, physical activity, and sleep.
Tracking Fat, Fiber, and Protein
Meals and Snacks:
- Breakfast, Lunch, Dinner, and Snacks: For each meal and snack throughout the day, record the types of food you consume.
- Fat, Fiber, and Protein: For each food item, note the approximate amount of fat, fiber, and protein it contains. Use nutritional labels, food tracking apps, or reliable online databases to determine these values. If you're eating homemade meals, estimate based on the ingredients used.
Quantifying Intake:
- Fat: Measure in grams. Note if the fats are saturated, unsaturated, or trans fats.
- Fiber: Measure in grams. Differentiate between soluble and insoluble fiber if possible.
- Protein: Measure in grams. Include both animal and plant-based protein sources.
Daily Totals:
- At the end of each day, sum up the total grams of fat, fiber, and protein consumed. This helps you see if you are meeting your dietary goals for each macronutrient.
TIPS FOR EFFECTIVE FOOD TRACKING
Start Simple: If you’re new to food tracking, start by simply writing down everything you eat and drink. You can gradually start adding more details as you get used to the process.
Be Honest: It’s important to record everything accurately, even if you overeat or consume unhealthy foods. This honesty will provide you with the most beneficial insights.
Include Context: Sometimes, the context in which you eat is as important as what you eat. Note if you’re eating out of hunger, stress, boredom, or social obligations.
Utilize Technology: Leverage technology to make tracking easier. Many apps not only track what you eat but also provide nutritional breakdowns and personalized feedback.
Food tracking is a powerful tool for gaining insight into your dietary habits and their impact on your health. By consistently monitoring what you eat, you can make informed decisions that enhance your nutritional well-being, manage health conditions, and improve overall quality of life. Whether manually using a journal or digitally with an app, the discipline of food tracking can lead to significant health benefits and a deeper understanding of the relationship between your diet and health.
This page contains affiliate links. This means I may earn a commission should you choose to sign up for a program or make a purchase using my link.
Mood Tracking
Enhancing Health through Dietary Awareness
Why Track Your Mood?
The connection between the gut and the brain, often referred to as the gut-brain axis, underscores the profound impact our digestive health has on our mental state, and vice versa. By tracking our mood alongside our diet and bowel habits, we can uncover patterns and triggers that affect our emotional and physical health.

PURPOSE OF Mood TRACKING
In the holistic approach of the Food, Mood, Poop Journal (FMPJ), mood tracking plays an essential role. This component is not just about recording emotions; it's about understanding the complex interplay between what we eat, how we digest it, and how it affects our mental and emotional health. Here’s why mood tracking is a crucial part of this comprehensive health tool:
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain axis is a well-documented pathway that highlights the bidirectional communication between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. The state of our gut health can significantly influence our mood and cognitive functions, and vice versa. By tracking our mood, we can gain insights into how our dietary choices and digestive health may be affecting our emotional well-being.
Key Purposes of Mood Tracking in the FMPJ:
Identifying Patterns: Mood tracking helps identify patterns and correlations between diet, bowel health, and emotional states. For instance, consuming certain foods might consistently lead to feelings of anxiety or depression, or a healthy gut might correlate with increased feelings of happiness and vitality.
Enhancing Dietary Adjustments: By observing how specific foods influence mood, users of the journal can make more informed decisions about dietary changes that may enhance their emotional and physical health.
Improving Mental Health Management: Regular mood tracking can lead to better management of stress, anxiety, and mood swings. It provides a clearer picture of what triggers negative moods and what practices or foods help maintain a positive emotional state.
Supporting Medical and Therapeutic Interventions: For those working with healthcare providers on managing a health condition, mood tracking can offer valuable data that may assist in tailoring treatments or therapies more effectively.
Promoting Mindfulness and Self-Awareness: The act of mood tracking encourages individuals to become more mindful of their emotional shifts and more aware of how their body and mind interact. This awareness can foster greater emotional intelligence and resilience.
What to Note and Why It Matters
Mood tracking involves a detailed recording of both your emotional and physical states throughout the day. It's an integral part of understanding your overall health, as emotions can profoundly influence physical health and vice versa. Here’s a closer look at what mood tracking entails and the specifics you should pay attention to.
What Does Mood Tracking Include?
Mood tracking isn't just about noting when you feel happy or sad; it's about capturing a wide range of physical sensations and emotional responses to provide a holistic view of your well-being. Here’s what to consider:
- **Emotional State**: Note any feelings of happiness, sadness, anxiety, or anger. Even subtle emotions like feeling content, uneasy, or nostalgic are important.
- **Physical Sensations**: Physical health can directly impact your mood. Record any physical symptoms that might not seem directly related to mood but can provide context to your emotional state.
- **Intensity and Frequency**: How intense are your emotions or physical sensations? How often do they occur? Identifying patterns can help pinpoint triggers or underlying health issues.
Specific Aspects to Track
To get the most out of mood tracking, it's crucial to be as detailed and specific as possible. Here are some key aspects to pay attention to:
- **Aches and Pains**: Any kind of pain, whether it's a mild headache or more severe pains like joint or back pain, can affect your mood and is worth tracking.
- **Fatigue and Sleep Patterns**: Note any feelings of tiredness, instances of insomnia, or if you're sleeping more than usual. Sleep has a significant impact on emotional regulation and overall health.
- **Digestive Symptoms**: Bloating, gas, and other digestive issues can be signs of food sensitivities or other health problems that might affect your mood.
- **Mood Swings**: Pay attention to any sudden shifts in mood, such as irritability or bursts of emotion, and what might be triggering them.
- **Headaches and Cramps**: These can be indicators of stress or hormonal changes and may correlate with mood changes.
- **Respiratory Symptoms**: Like a sore throat, which could suggest an onset of illness affecting your mood.
- **Edema**: Swelling or bloating in the body can cause discomfort and affect how you feel emotionally.
- **Skin Conditions**: Skin issues like acne or eczema can be exacerbated by stress or dietary factors and may impact self-esteem and mood.
- **Cognitive Changes**: Note any occurrences of brain fog or forgetfulness, which can be linked to diet, sleep quality, or emotional stressors.
#### How to Track Effectively
- **Be Observant**: Throughout the day, periodically check in with yourself. How do you feel? What are you experiencing physically and emotionally?
- **Use a Journal or App**: A dedicated mood tracking journal or a mobile app can help you consistently log your emotions and physical sensations.
- **Review Regularly**: Make it a habit to review your entries regularly. This can help you identify patterns or triggers that affect your mood and physical well-being.
- **Seek Patterns**: Over time, you'll start to see patterns that can help you make connections between your lifestyle choices and how you feel. This insight can be invaluable for making changes to improve your health.
Mood tracking is a powerful tool in your health and wellness toolkit. By meticulously noting both your emotional and physical states, you can gain insights into how your body and mind interact. This awareness can guide you in making informed decisions about managing stress, dietary choices, and other lifestyle factors that influence your overall health.
WHAT TO LOOK FOR WHEN TRACKING MOOD
Emotional States: Record your feelings throughout the day at regular intervals. Note any predominant emotions like happiness, sadness, anxiety, or irritability.
Intensity and Duration: Mark the intensity of your emotions on a scale (e.g., 1-10) and note how long certain moods last.
Contextual Factors: Consider what might be influencing your mood. Did you eat something unusual? Did you sleep poorly? What’s happening in your personal life?
BENEFITS OF Mood TRACKING
Enhanced Self-Awareness: Regular mood tracking can increase your awareness of emotional states and triggers, helping you manage stress, anxiety, and depression more effectively.
Correlation with Diet and Gut Health: By observing how your mood changes in relation to food intake and digestive health, you can identify foods that might be affecting your mood, for better or worse.
Improved Mental Health Management: With detailed mood data, you can better understand what factors contribute to mood swings or emotional dips, leading to more effective coping strategies.
Getting the Most Out of Your Journal
To effectively use the Food, Mood, Poop Journal, commit to making regular entries and be as detailed as possible. Consistency is key to uncovering patterns and making the necessary adjustments to improve your health. Each week, take time to review your entries, note any trends, and consider how you might adapt your diet and lifestyle to foster better gut health.
This journal not only serves as a daily log but also as a guide to educate you on the importance of each tracked aspect and how they interrelate.
The Food, Mood, Poop Journal is an invaluable resource for anyone looking to enhance their digestive health, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. By integrating this tool into your daily routine, you embark on a path of greater self-awareness and proactive health management, leading to a healthier, more balanced you
HOW TO TRACK YOUR MOOD EFFECTIVELY
Regular Entries: Aim to jot down your mood several times a day—perhaps in the morning, afternoon, and evening—to capture any fluctuations.
Be Detailed and Consistent: The more information you provide, the more useful your mood tracking will be. Consistency is key to identifying patterns over time.
Integrate with Food and Poop Tracking: Align your mood data with what you eat and your digestive health to see how they might influence your emotional state.
Use Tools and Apps: While a simple journal works, numerous apps can help track your mood, offering analytics and reminders to log your feelings.
Approach this with an open mind and without judgment. Each entry helps paint a more complete picture of your health, showing how interconnected our diets, digestion, and emotions truly are.
Mood tracking is more than just noting how you feel; it’s about understanding and managing the interplay between your mind and body. By incorporating mood tracking into your daily routine, you create a powerful tool for personal growth and health optimization, paving the way for a balanced and emotionally resilient life. Let’s move forward with curiosity and mindfulness, eager to discover how our bodies and minds respond to the world around us.
This page contains affiliate links. This means I may earn a commission should you choose to sign up for a program or make a purchase using my link.
Poop Tracking
Find out what your stool has to say about your Health
Why Track Your Poop?
Understanding the nuances of your digestive health is a critical aspect of maintaining overall wellness, and tracking your poop offers direct insights into the functioning of your gut. While it may initially seem uncomfortable or trivial, the information derived from observing your bowel movements is invaluable for identifying potential health issues, optimizing your diet, and understanding how your body responds to various foods, stressors, and lifestyle changes. Here’s a deeper dive into why tracking your poop is an essential health practice:
Key Reasons to Track Your Poop
1. Indicator of Gut Health: Your stool is a direct reflection of the health of your digestive system. Changes in the consistency, frequency, and appearance of your bowel movements can signal disturbances in your gut flora, potential infections, or digestive disorders.
2. Early Detection of Digestive Disorders: Regular tracking can help catch early signs of conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and even colorectal cancer. Early detection is crucial for effective management and treatment.
3. Impact of Diet on Digestion: By monitoring changes in your stool, you can see how different foods affect your digestion. For example, an increase in fiber might change stool bulk and frequency, whereas dairy or gluten might cause discomfort or changes in stool consistency if you're intolerant.
4. Absorption of Nutrients: The appearance of undigested food in your stool can indicate malabsorption, suggesting that your body isn’t properly absorbing the nutrients from your food. This can be critical for addressing dietary needs or underlying conditions like celiac disease or pancreatic insufficiency.
5. Hydration Status: Your stool can also reflect your hydration status; hard, dry stools may suggest you need to drink more water, while very loose stools might indicate dehydration or other issues.
6. Effectiveness of Probiotics or Medications: If you're taking probiotics or certain medications, observing changes in your bowel habits can help determine if these interventions are effective.
By tracking your poop, you can gain valuable insights into your digestive health and make informed decisions to improve your overall well-being. Regular monitoring can help you identify issues early, understand the impact of dietary choices, and ensure your gut is functioning optimally.

What to Track
When tracking your poop, consider the following aspects for a comprehensive view:
- Frequency: Note how often you go. Deviations from your norm can be significant.
- Form and Consistency Use the Bristol Stool Chart as a guideline to classify the form of your stools.
- Color: Colors can indicate various health states. For example, black or red may suggest gastrointestinal bleeding, and very pale stools could indicate bile duct obstruction.
- Size and Amount: Changes in the size and amount can indicate variations in dietary intake or issues in digestive function.
- Odor: An unusually strong odor can sometimes indicate infections or complications.
- Presence of Blood or Mucus: This could be a sign of inflammation, infection, or colorectal cancer.
Introducing the Bristol Stool Chart
Enhancing Health Tracking with the Food, Mood, Poop Journal (FMPJ)
As part of our comprehensive approach to health monitoring through the Food, Mood, Poop Journal (FMPJ), we introduce an invaluable tool for evaluating digestive health: the Bristol Stool Chart. This chart is not just a clinical resource; it’s a practical guide that can help anyone become more attuned to their digestive health by providing a clear, visual method to categorize bowel movements.
What is the Bristol Stool Chart?
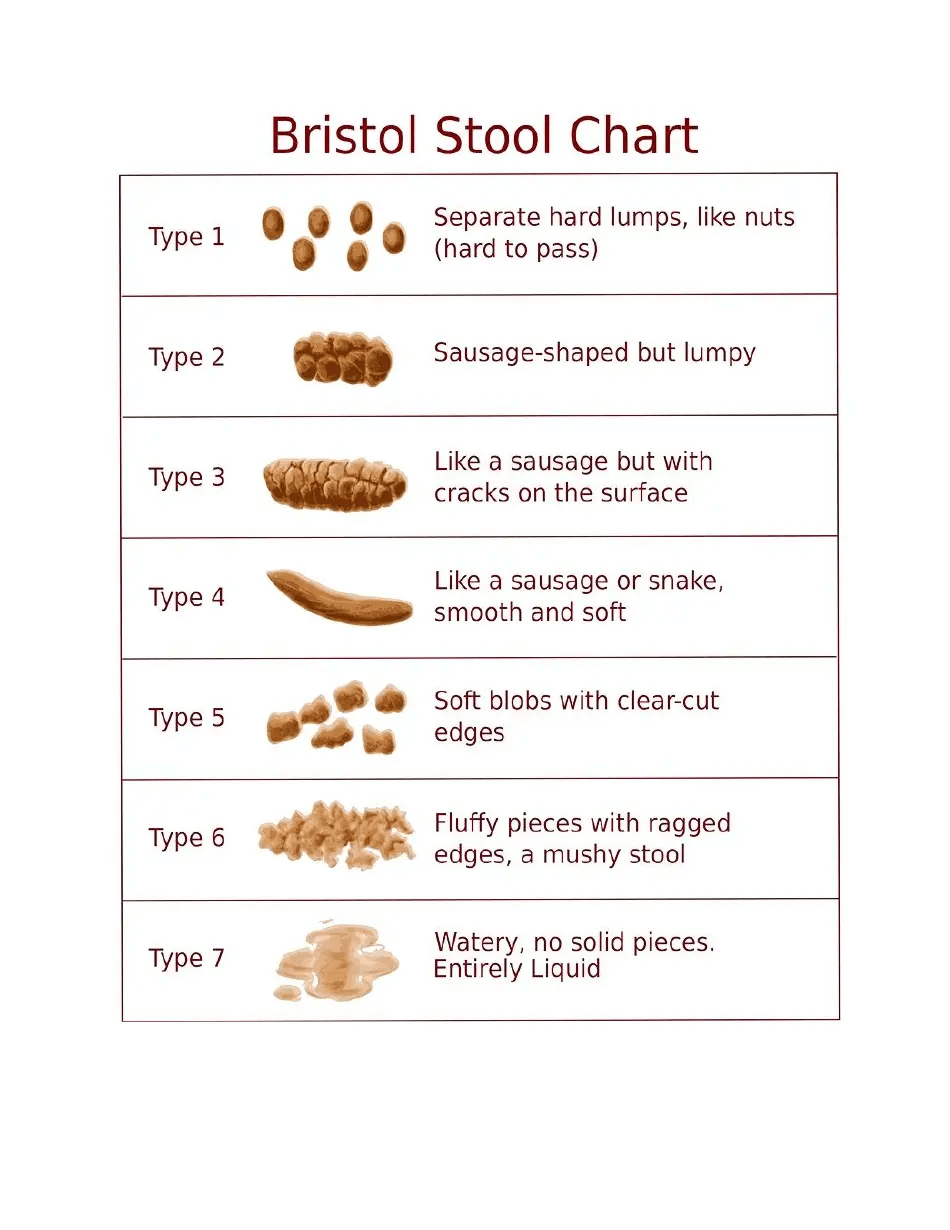
The Bristol Stool Chart is a diagnostic medical tool developed by Dr. Ken Heaton at the University of Bristol. It classifies human feces into seven categories, each of which provides information about different balance or imbalance states in the gut. The categories range from Type 1, which indicates severe constipation, to Type 7, which indicates diarrhea.
Types of Stool in the Bristol Stool Chart
- Type 1: Separate hard lumps, like nuts (hard to pass) - indicates severe constipation.
- Type 2: Sausage-shaped but lumpy - suggests slightly less severe constipation.
- Type 3: Like a sausage but with cracks on its surface - normal.
- Type 4: Like a sausage or snake, smooth and soft - optimal.
- Type 5: Soft blobs with clear-cut edges (easy to pass) - normal but tending towards diarrhea.
- Type 6: Fluffy pieces with ragged edges, a mushy stool - mild diarrhea.
- Type 7: Watery, no solid pieces, entirely liquid - severe diarrhea.
How the Bristol Stool Chart Enhances the FMPJ
Using the Bristol Stool Chart in conjunction with the FMPJ allows for precise tracking and analysis of bowel health. Here’s how it enhances the tracking process:
- Clarity and Accuracy: The chart provides a visual reference that helps you accurately describe your stool, which is crucial for identifying health trends or concerns.
- Early Detection of Issues: Regular tracking can help catch deviations from your normal stool type, which might indicate dietary issues or health problems needing attention.
- Diet and Health Correlations: By correlating changes in stool types with dietary intake or emotional states logged in the FMPJ, you can identify foods or stressors that affect your digestive health.
- Communication with Healthcare Providers: Accurate stool descriptions using the chart can help your healthcare provider make better-informed decisions, enhancing the care you receive.
How to Use the Bristol Stool Chart with the FMPJ
- Daily Tracking: Each day, record your stool type according to the Bristol Stool Chart in the FMPJ.
Introducing the Bristol Stool Chart
Enhancing Health Tracking with the Food, Mood, Poop Journal (FMPJ)
As part of our comprehensive approach to health monitoring through the Food, Mood, Poop Journal (FMPJ), we introduce an invaluable tool for evaluating digestive health: the Bristol Stool Chart. This chart is not just a clinical resource; it’s a practical guide that can help anyone become more attuned to their digestive health by providing a clear, visual method to categorize bowel movements.
What is the Bristol Stool Chart?
The Bristol Stool Chart is a diagnostic medical tool developed by Dr. Ken Heaton at the University of Bristol. It classifies human feces into seven categories, each of which provides information about different balance or imbalance states in the gut. The categories range from Type 1, which indicates severe constipation, to Type 7, which indicates diarrhea.
Types of Stool in the Bristol Stool Chart
- Type 1: Separate hard lumps, like nuts (hard to pass) - indicates severe constipation.
- Type 2: Sausage-shaped but lumpy - suggests slightly less severe constipation.
- Type 3: Like a sausage but with cracks on its surface - normal.
- Type 4: Like a sausage or snake, smooth and soft - optimal.
- Type 5: Soft blobs with clear-cut edges (easy to pass) - normal but tending towards diarrhea.
- Type 6: Fluffy pieces with ragged edges, a mushy stool - mild diarrhea.
- Type 7: Watery, no solid pieces, entirely liquid - severe diarrhea.
How the Bristol Stool Chart Enhances the FMPJ
Using the Bristol Stool Chart in conjunction with the FMPJ allows for precise tracking and analysis of bowel health. Here’s how it enhances the tracking process:
- Clarity and Accuracy: The chart provides a visual reference that helps you accurately describe your stool, which is crucial for identifying health trends or concerns.
- Early Detection of Issues: Regular tracking can help catch deviations from your normal stool type, which might indicate dietary issues or health problems needing attention.
- Diet and Health Correlations: By correlating changes in stool types with dietary intake or emotional states logged in the FMPJ, you can identify foods or stressors that affect your digestive health.
- Communication with Healthcare Providers: Accurate stool descriptions using the chart can help your healthcare provider make better-informed decisions, enhancing the care you receive.
How to Use the Bristol Stool Chart with the FMPJ
- Daily Tracking: Each day, record your stool type according to the Bristol Stool Chart in the FMPJ.
- Note Variations: Pay attention to any changes in stool type and note possible causes such as diet changes, stress levels, illness, or medication.
- Review Patterns: Regularly review your entries to identify any patterns or recurring issues that may require dietary adjustments or medical intervention.
The Bristol Stool Chart is a simple yet powerful tool that complements the Food, Mood, Poop Journal by providing crucial insights into gut health. By incorporating this chart into your daily health tracking, you enhance your ability to monitor and respond to changes in your digestive system, leading to better health management and overall well-being. With this tool, you’re not just tracking your health; you’re taking an active step towards improving it.
Integrating Poop Tracking into Your Routine
To effectively integrate poop tracking into your health routine:
- Maintain a Daily Log: Consistency is key in tracking, so make it a part of your daily routine.
- Review Patterns: Regularly look back over your logs to identify any patterns or changes. Discuss these with a healthcare provider if anything unusual arises.
- Combine with Other Health Data: Link your poop tracking with food and mood logs to get a holistic view of your health influences and outcomes.
Tracking your poop provides critical insights that are vital for maintaining digestive health and, by extension, your overall well-being. By understanding the signals your body sends through bowel movements, you can make informed decisions about dietary choices, lifestyle changes, and medical care, leading to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
Getting the Most Out of Your Journal
To effectively use the Food, Mood, Poop Journal, commit to making regular entries and be as detailed as possible. Consistency is key to uncovering patterns and making the necessary adjustments to improve your health. Each week, take time to review your entries, note any trends, and consider how you might adapt your diet and lifestyle to foster better gut health.
This journal not only serves as a daily log but also as a guide to educate you on the importance of each tracked aspect and how they interrelate.
The Food, Mood, Poop Journal is an invaluable resource for anyone looking to enhance their digestive health, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. By integrating this tool into your daily routine, you embark on a path of greater self-awareness and proactive health management, leading to a healthier, more balanced you
Poop Stats
Typically, about 50% of the stomach's contents are emptied within 2.5 to 3 hours after eating. Complete emptying of the stomach generally takes around 4 to 5 hours.
Once food reaches the small intestine, 50% of it is usually processed within 2.5 to 3 hours. The transit through the colon happens within approximately 16 to 40 hours after eating. It is important to note that a shorter transit time is generally beneficial, but it shouldn't be so rapid that it compromises nutrient assimilation.
It is normal for a healthy person eating three meals a day to have between one and three bowel movements per day. Three poops per day would be ideal. Some experts provide a normal range of three bowel movements per day to three bowel movements per week. We like to see between one and three per day as a good measure of digestive function and detoxification.
Constipation is a common problem in the US. Some research suggests that the majority of adults have far less than three movements per day. This means that they are retaining waste products inside their body.
Digestion is one of the biggest stresses we place on our body daily. When the digestive system is already burdened by factors like dysbiosis, toxins, allergens, sensitivities, or chronic stress, the process of digestion can add even more strain to an already overtaxed system.
This page contains affiliate links. This means I may earn a commission should you choose to sign up for a program or make a purchase using my link.
Functional Diagnostic Nutrition® health coaches do not diagnose, treat, prevent, or cure any
disease or condition. Nothing we share with our clients is intended to substitute for the advice,
treatment or diagnosis of a qualified licensed physician. Functional Diagnostic Nutrition® (FDN)
Practitioners may not make any medical diagnoses or claim, nor substitute for your personal
physician’s care. It is the role of a Functional Diagnostic Nutrition® Practitioner to partner with
their clients to provide ongoing support and accountability in an opt-in model of self-care and
should be done under the supervision of a licensed physician.