Emotional intelligence, a term gaining popularity in the 1990s through Daniel Goleman's writings, challenges the traditional view of IQ as the sole determinant of success. Researchers like Peter Salavoy and John Mayer introduced the concept after noticing individuals with average IQs frequently outperforming those with higher IQs, attributing this phenomenon to emotional intelligence. This critical factor encompasses both intrapersonal intelligence—our ability to understand and manage our own emotions—and interpersonal intelligence, which involves our capacity to connect with and understand others within social contexts.
The development of emotional intelligence involves a complex process of rewiring the brain to improve personal communication and the interpretation of emotional signals. This process emphasizes the cooperation between the emotional and rational parts of the brain, highlighting that both our emotions and how we interpret them play crucial roles in decision-making. Embracing the duality of emotions, the article argues for a balanced approach that neither dismisses emotions as irrational nor blindly trusts them, but rather advocates for mindful awareness and interpretation as a pathway to better decision outcomes.
The practice of mindfulness is presented as a transformative tool to increase emotional intelligence. By encouraging a pause between feeling and reaction, individuals can assess the accuracy of their emotional responses and ensure their actions align with their values and goals. This approach not only fosters personal growth and improved self-awareness but also enhances interpersonal relationships through more effective communication and empathy. The journey toward emotional intelligence, while demanding practice and dedication, ultimately leads to a more mindful and fulfilling life.
Read more...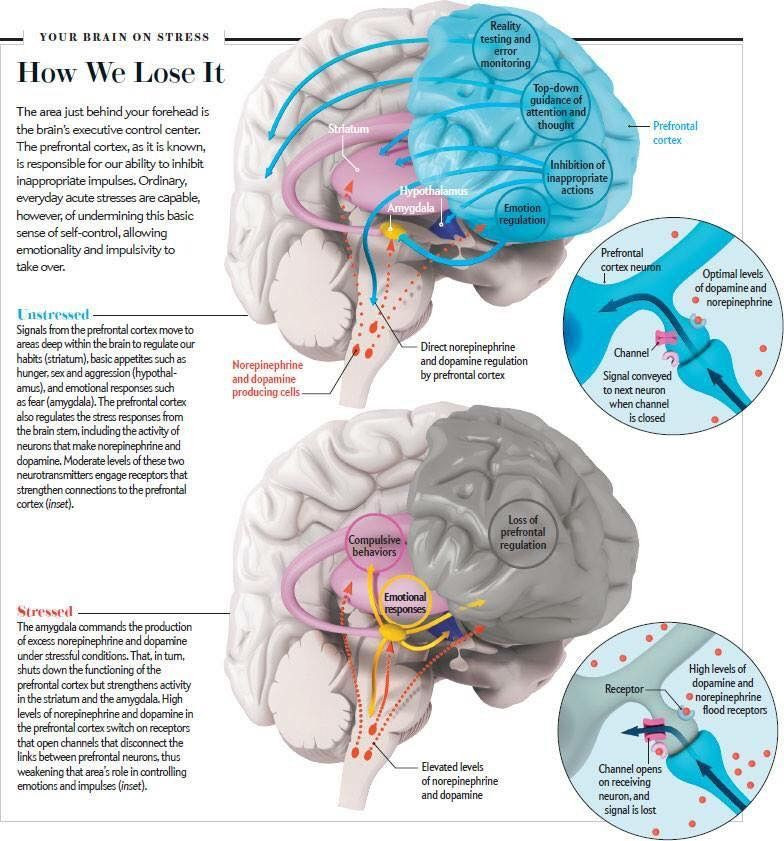
This blog post discusses how trauma can impact the brain and body. Research has shown that trauma can cause changes in key brain regions, including the hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex, which can impact memory, emotion processing, and decision-making. Additionally, trauma can impact the stress response system, leading to a dysregulated stress response and increased sensitivity to stress. These effects can contribute to the development of mental health disorders such as PTSD and anxiety.
Read more...



